STYE SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
Signs and symptoms of a stye (medical term: hordeolum) may vary from person to person. But most stye sufferers experience the same features that are regarded as typical indications of an eye stye. The following conditions suggest the probable presences of a developing stye:
- Eyelid pain
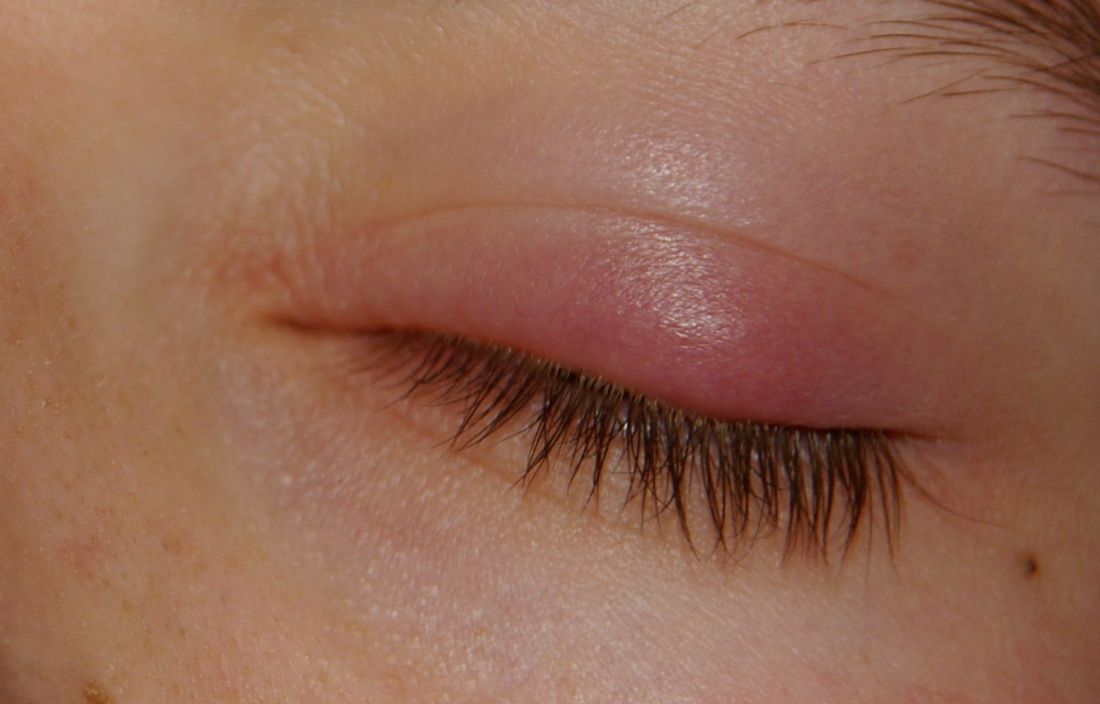
- Localized swelling of the eyelid
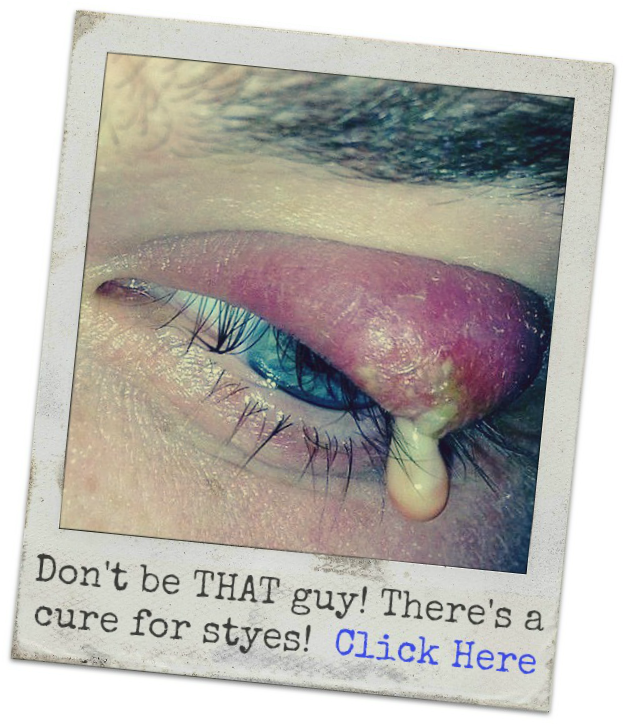
- Mucus discharge on the eyelid margins
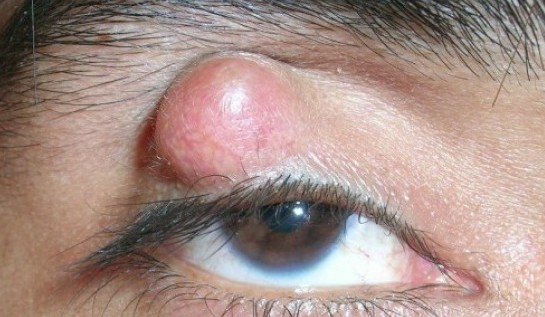
- Bump on the bottom or top eyelid
EYELID PAIN
The first sign of an emerging stye is the presence of pain in the infected eyelid. Stye pain is generally restricted to the specific area of growth, but the pain can expand into the cheek area below the eye if the infection spreads to the surrounding tissue.
The first sign of eyelid pain is felt when blinking or rubbing the affected eye. The initial pain is characterized as a small stingy sensation, but develops into a persistent soreness as the abscess matures. Tylenol or generic versions of Acetaminophen are effective at reliving eyelid pain. While acetaminophen is successful at alleviating eyelid pain, it’s not effective in reducing inflammation.
The first sign of eyelid pain is felt when blinking or rubbing the affected eye. The initial pain is characterized as a small stingy sensation, but develops into a persistent soreness as the abscess matures. Tylenol or generic versions of Acetaminophen are effective at reliving eyelid pain. While acetaminophen is successful at alleviating eyelid pain, it’s not effective in reducing inflammation.
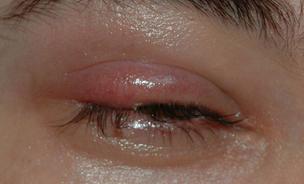
LOCALIZED EYELID SWELLING
Eyelid swelling is the next symptom of a developing stye. Localized swelling is caused by accumulation of fluid in a specific part of the eyelid tissue. Eyelids often become so swollen that the lid has the appearance of drooping, and can cause visual problems.
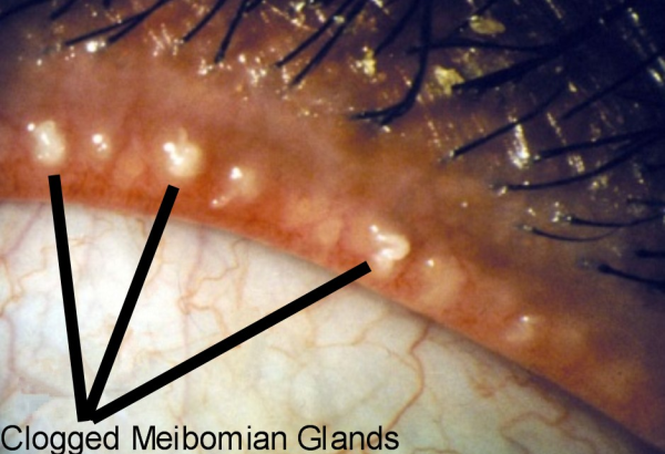
Eye styes are a common eyelid problem that are caused by bacterial infection to the oil glands (known as meibomian glands). Styes also arise due to inflammatory eyelid disease such as blepharitis.
Eye styes are a common eyelid problem that are caused by bacterial infection to the oil glands (known as meibomian glands). Styes also arise due to inflammatory eyelid disease such as blepharitis.
There are approximately 20 to 40 meibomian glands in each eyelid. The meibomian glands function is to secret oil, which then mixes with our tears and prevents tear evaporation. A stye occurs when one of these oil glands becomes infected and subsequently blocked.
Treatment for eyelid swelling consist of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen. Consult a doctor before taking this medicine if you’ve had reactions to other anti-inflammatory painkillers.
Treatment for eyelid swelling consist of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen. Consult a doctor before taking this medicine if you’ve had reactions to other anti-inflammatory painkillers.
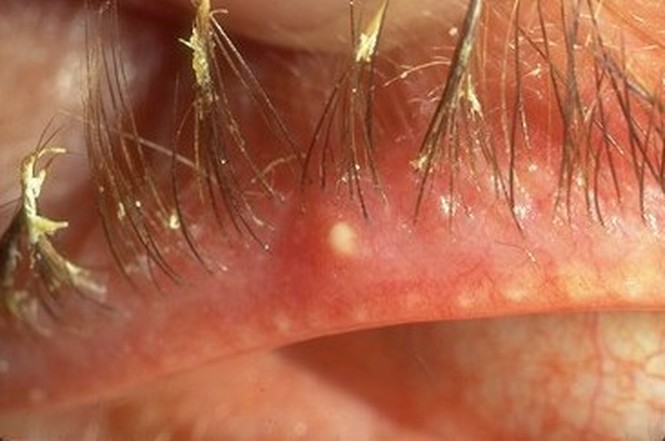
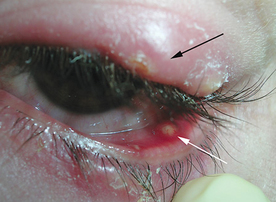
DISCHARGE ON THE EYELID MARGIN
A stye is a blockage of the meibomian gland at the edge of the eyelid, and is often caused by an infected eyelash follicle. Eyelid crusting, pus and and discomfort usually occurs as a result.
Eye discharge (slang names: eye gunk, eye pus, eye boogers) is a combination of skin cells, mucus, oil and other debris that accumulate on the eyelid margins or eyelashes during sleep. Discharge can be crusty, sticky or wet, depending on how much liquid in the discharge evaporates.
Eye discharge (slang names: eye gunk, eye pus, eye boogers) is a combination of skin cells, mucus, oil and other debris that accumulate on the eyelid margins or eyelashes during sleep. Discharge can be crusty, sticky or wet, depending on how much liquid in the discharge evaporates.
Excessive eye discharge could indicate disease or an eye infection, such as a stye. In some instances, eyelid crusting can become so severe that it locks the eyelids together during sleep.
BUMP ON THE EYELID
After the swelling has subsided, a pronounced bump becomes visible on the eyelid. A bump on the eyelid is a good indication a stye is present.
A stye appears as a red bump on the eyelid and resembles a pimple or zit. It’s caused by blockage of an oil gland. Most styes develop over a few days, then drain and heal on their own.
If the stye doesn’t ooze pus from the meibomian gland opening, or burst though the inner or outer surface of the eyelid, a chlazion can form. A chalazion is oil gland that becomes fully blocked. Chalazions can appear as a large bump, up to the size of a pea. If more than one gland contains blockage, the lump can grow even larger. A ophthalmologist can perform a simple surgery to remove the chalazion.
A stye appears as a red bump on the eyelid and resembles a pimple or zit. It’s caused by blockage of an oil gland. Most styes develop over a few days, then drain and heal on their own.
If the stye doesn’t ooze pus from the meibomian gland opening, or burst though the inner or outer surface of the eyelid, a chlazion can form. A chalazion is oil gland that becomes fully blocked. Chalazions can appear as a large bump, up to the size of a pea. If more than one gland contains blockage, the lump can grow even larger. A ophthalmologist can perform a simple surgery to remove the chalazion.